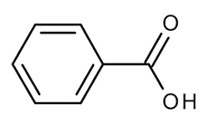
Benzoic acid is the simplest aromatic carboxylic acid.
Natural Sources of Benzoic acid:
Benzoic acid was isolated in the sixteenth century, but not commercially produced until the end of the nineteenth century. Its antimicrobial properties were discovered in the 1875, leading to its widespread use as a food preservative [1].
Benzoic acid can be found naturally in edible plants such as Cranberry and Cinnamon[2], cloves [3] and other fruits and berries.
Mechanism of Action:
Benzoic acid has shown itself to interact through numerous mechanisms to prevent the growth of microorganisms. Two of the most common ones are listed below [4]:
1) pH reduction: Benzoic acid is a weak acid, meaning it dissociates into its ionized form (benzoate ion) and hydrogen ions (H+) in solution. The presence of benzoic acid can decrease the pH of the environment, making it more acidic. This can result in disruption of the cell membrane.
2) Acidification if internal cell environment: Benzoic acid, with a pKa of 4.19, exists primarily in its undissociated form at low pH. This form easily crosses cell membranes, but once inside the cell (pH 6-7), it dissociates. The resulting anion accumulates inside the cell, potentially acidifying the cytosol and inhibiting growth.
Safety information Summary:
| LD50 Oral | 2360 mg/kg | [5] |
| LD50 Dermal | >2000 mg/kg | [5] |
| NOAEL | 800 mg/kg bw/d | [6] |
| Skin irritant | Irritating to the skin | [5] |
| Eye Irritant | Irritating to the eyes | [5] |
| Mucous membrane irritation | Negative | [5] |
| Skin sensitization | Negative | [5] |
| Mutagenicity | Negative | [5] |
[1] J. R. Chipley, “Antimicrobials in Food”, CRC Press, 4th addition, 2020, pp.48
[2] Zylkiewicz et.al., “Biologically Active Compounds of Plants: Structure-Related Antioxidant, Microbiological and Cytotoxic Activity of Selected Carboxylic Acids” Materials, 13, 2020, pp. 4454
[3] Kiran et al.,“Isolation of secondary metabolites from Syzygium aromaticum (L.) Merr. & L.M.Perry. (cloves), and evaluation of their biological activities”, Nat. Prod. Res., vol. 37 (12), 2023, pp. 2018
[4] Hazan et al.,“Benzoic Acid, a Weak Organic Acid Food Preservative, Exerts Specific Effects on Intracellular Membrane Trafficking Pathways in Saccharomyces cerevisiae” Appl Environ Microbiol., vol .70(8), 2004, pp. 4449–4457
[5] Benzoic Acid, Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS), 2023-07-19 version 5, Carl Roth GmbH, Schömperlenstraße 3-5, D-76185, Karlsruhe, 28.08.2015
[6] “Final report on the safety assessment of Benzyl Alcohol, Benzoic Acid, and Sodium Benzoate”, Int J Toxicol, 20 Suppl 3, 2001, pp. 23-50.
